Research
Quantum-dot Plasmon Lasers
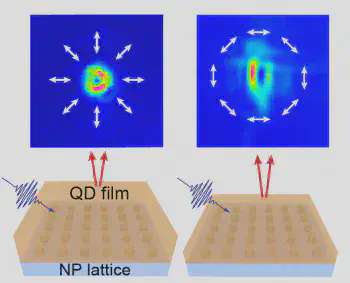
We construct nanoscale lasers using novel light-emitting materials and plasmonic cavities. By near-field coupling of colloidal quantum dots (QDs) to metal nanoparticle lattices, we realized compact lasers with submicron device thicknesses. In contrast to current techniques that rely on bulky optical elements to achieve laser polarization control, this QD-plasmon hybrid material system can serve as a nanoscale light source to generate desired lasing polarization patterns. We also revealed that high-symmetry points in the reciprocal space of plasmonic nanoparticle lattices can support lasing at well-defined angles. By changing the periodicity of the plasmonic lattices or the thickness of the QD film, we engineered the optical band structure for controllable lasing direction. Our work offers critical insights into how to manipulate the interaction between quantum emitters and optical cavities at the nanoscale, and offers prospects for applications in quantum communication and information.
References:
- J. Guan, L.K. Sagar, R. Li, D. Wang, G. Bappi, W. Wang, N. Watkins, M.R. Bourgeois, L. Levina, F. Fan, S. Hoogland, O. Voznyy, J. Martins de Pina, R.D. Schaller, G.C. Schatz, E.H. Sargent, and T.W. Odom, “Quantum Dot-Plasmon Lasing with Controlled Polarization Patterns.” ACS Nano 14, 3426-3433 (2020).
- J. Guan, L.K. Sagar, R. Li, D. Wang, G. Bappi, N.E. Watkins, M.R. Bourgeois, L. Levina, F. Fan, S. Hoogland, O.Voznyy, J.M. de Pina, R.D. Schaller, G.C. Schatz, E.H. Sargent, and T.W. Odom, “Engineering Directionality in Quantum Dot Shell Lasing Using Plasmonic Lattices.” Nano Letters 20, 1468-1474 (2020).
Plasmonic Metasurface Design
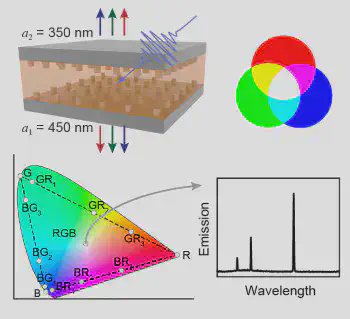
We exploit the design of plasmonic metasurfaces to realize multifunctional nanolasers. Through the discoveries of new optical modes – light-cone surface lattice resonances – in metal nanoparticle lattices, we have reported multi-color, in-plane emission from nanometer-scale thin laser devices. This study offers a design strategy to realize real-time tunable lasing colors by lattice rotation, which is not possible in conventional lasers. We also realized a simultaneous red, green, and blue laser by combining a sandwiched lattice structure with a mixed dye solution. Our work showed how lasing colors can be manipulated in compact architectures, which will be useful for display technologies, on-chip optical communications, and light-induced chemical reactions.
References:
- J. Guan, J-E. Park, S. Deng, M. J. H. Tan, J. Hu, and T. W. Odom, “Light-Matter Interactions in Hybrid Material Metasurfaces.” Chemical Reviews 122, 15177-15203 (2022).
- J. Guan, R. Li, X. G. Juarez, A. Sample, Y. Wang, G. C. Schatz, and T. W. Odom, “Plasmonic Nanoparticle Lattice Devices for White-Light Lasing.” Advanced Materials 2103262 (2021).
- J. Guan, M. R. Bourgeois, R. Li, J. Hu, R. D. Schaller, G. C. Schatz, and T. W. Odom, “Identification of Brillouin Zones by In-Plane Lasing from Light-Cone Surface Lattice Resonances.” ACS Nano 15, 5567−5573 (2021).
Moiré Photonic Phenomena
The combination of multiple periodic structures to create moiré patterns holds great potential for controlling and manipulating light. However, the effects and interactions associated with moiré patterns have been limited to the immediate vicinity of these patterns. We present our observations of a remarkable phenomenon: the ultralong-range coupling between photonic lattices in bilayer and multilayer moiré architectures. We show that two-dimensional plasmonic nanoparticle lattices enable twist-angle-controlled, directional lasing emission, even when the lattices are spatially separated by distances exceeding three orders of magnitude that of the lattice periodicity. The discovery of this far-field, inter-lattice coupling opens up exciting possibilities for utilizing the out-of-plane dimension to manipulate light on a nanoscale and microscale level.
References:
- J. Guan, J. Hu, Y. Wang, M. J. H. Tan, G. C. Schatz, and T. W. Odom, “Far-field Coupling between Moiré Photonic Lattices.” Nature Nanotechnology 18, 514-520 (2023).